
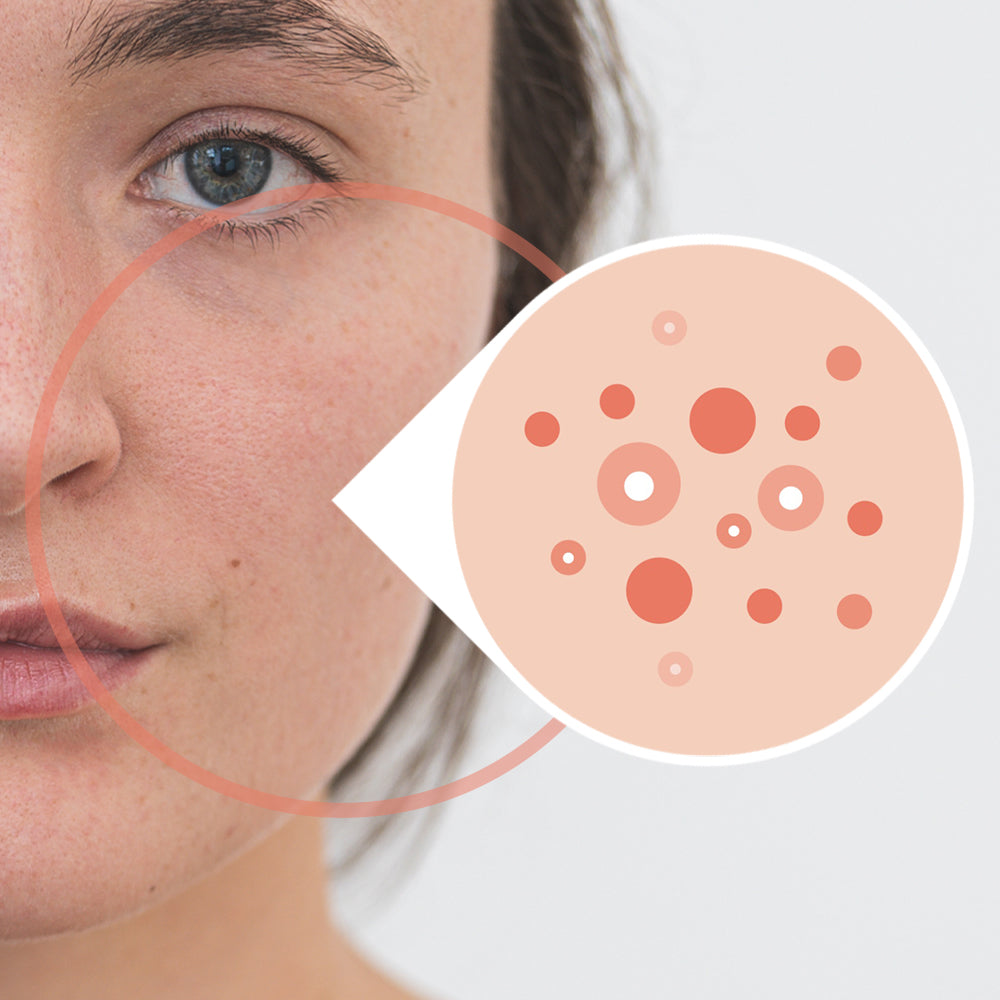
WHAT IS ACNE?
Acne appears in various forms, typically manifesting as pustules, pimples, and blackheads (comedones) on the face, particularly on the forehead, nose, chin, and cheeks. There are different types of acne, with acne vulgaris—also known as "common acne"—being the most prevalent and widespread skin condition worldwide. It is non-contagious and especially common during puberty.
Approximately 70 to 95 percent of adolescents experience acne-related skin changes. About 15 to 30 out of every 100 adolescents suffer from moderate to severe acne, with boys being affected more frequently than girls. In some cases, acne persists into adulthood, even after puberty.
However, acne is not limited to the face and can also affect other parts of the body, such as the arms, back, and décolleté.
FORMS OF ACNE
The most commonly known type of acne is referred to by doctors as acne vulgaris, typically caused by hormonal changes during puberty. Boys are more commonly affected than girls. Acne vulgaris is classified into several types, based on the severity of the skin changes:
-
Acne comedonica: This is the mildest form of common acne. It typically appears on the face as blackheads (comedones), which can either be open or closed. If squeezed, these blackheads can become inflamed, turning into red nodules, which may develop into pustules.
-
Acne papulopustulosa: This moderate form of acne is characterized by a combination of blackheads and inflamed pimples. It often affects both the face and back. The term "papulopustulosa" is derived from papula (nodule) and pustula (pus-filled blister).
-
Acne conglobata: This is the most severe form of acne vulgaris, where pimples develop into large, inflammatory nodules, abscesses, crusts, and deep scars. It primarily affects men.
HOW DOES ACNE OCCUR?
During puberty, hormonal changes, particularly an increase in androgens, trigger changes in the body. Androgens are male sex hormones, though they are also produced in smaller amounts by the female body. These hormones stimulate the skin to produce more oil, called sebum. Sebum helps to keep the skin soft and provides a protective barrier. However, when sebum cannot drain properly, blackheads form. If these blackheads become infected, they can develop into acne pimples.
Acne primarily affects areas with a high concentration of sebaceous glands, such as the face, chest, back, and shoulders.
Not everyone who experiences pimples or acne will have persistent issues, suggesting that genetic factors and the immune system may also play a role in the development of acne.
WHAT CAUSES ACNE? WHAT ARE THE TRIGGERS OF ACNE?
The causes of acne, also known as triggers, can vary from person to person. It’s important to understand and observe your body and its reactions. Acne vulgaris is primarily caused by hormonal changes, commonly occurring during puberty but also during adulthood, pregnancy, or menopause. In addition to hormonal shifts, genetic predisposition and external factors can contribute to the development of acne. The following factors play a role in acne development:
-
-
Sebaceous Gland Hyperfunction
- Overproduction of sebum by the sebaceous glands.
-
Keratinization Disorders
- Disruption in the process of shedding dead skin cells, leading to blockages in sebaceous gland ducts.
-
Bacterial Overgrowth
- The growth of acne-causing bacteria in blocked pores.
-
Inflammatory Reactions
- Inflammation resulting from clogged pores and bacterial activity.
-
Psychological Stress
- Stress, grief, or excitement can trigger acne flare-ups.
-
Hormonal Factors
- Hormonal changes, such as during pregnancy, menstruation, or hormonal imbalances, can increase acne severity.
-
Substances on the Skin
- Skin-irritating cleaning agents, cosmetics, makeup, fragrances, and preservatives can contribute to breakouts.
- Lack of hygiene can also exacerbate acne.
-
Sugar and Carbohydrates
- Diets high in sugar and refined carbohydrates can increase insulin levels and promote acne development.
-
Tobacco Smoke and Consumption
- Smoking or exposure to tobacco smoke can worsen acne by increasing inflammation and clogging pores.
-
Medications
- Certain medications can trigger acne, including:
- Cortisone
- Anabolic Steroids
- Psychotropic Drugs
- Adrenocorticotropin (ACTH)
- Neuroleptics
- Halogens
- Antibiotics
- Vitamin B2, B6, B12
- Drugs for Cancer Treatment
-
CONSEQUENCES OF ACNE:
Scars may remain, particularly in cases of severe acne. These scars form as the wound heals. Acne can cause damage to the deeper layers of the skin, and as the skin heals, it does so in various ways. The scars may appear as small, flat, barely noticeable marks, or they could develop into more prominent dimples on the face. There are several types of acne scars, including:
-
Atrophic scars: These occur when the wound does not heal properly and too little connective tissue is produced. As a result, scars and depressions (pits) form beneath the surrounding tissue.
Hypertrophic scars: Raised scars may appear on the chest, back, or shoulders, particularly in cases of severe acne. These scars develop when excess connective tissue is produced during the healing process. However, hypertrophic scars are rare as a long-term consequence of acne.
Keloids: In some cases, an overproduction of connective tissue leads to keloids. Unlike hypertrophic scars, keloids extend beyond the initially inflamed area. They are a very rare consequence of acne.
Squeezing blackheads, pimples, and pustules can also result in scarring.
HOW IS ACNE TREATED?
The treatment options for acne are diverse and highly individual, which is why we’ll dedicate another article to this topic. In our next article, 'Acne Treatment Methods,' you’ll learn more about these approaches.
However, what we can share with you now is that natural treatments, such as using salt, can work wonders for this skin condition. You’ve probably noticed how your skin improves quickly during a summer vacation by the sea...
Salt Shower to Soothe the Skin

NATURAL CARE FOR PROBLEMATIC SKIN
THE ALTERNATIVE TO SALT BATHS FOR SENSITIVE, DRY AND REDDENED SKIN.
TO THE STARTER SETSHOWER+ FOR ACNE CARE
The Shower+ products are ideal for supporting acne treatment. Rather than drying out the skin, they hydrate it with the beneficial properties of salt. Sea salt not only cleanses the skin but also offers antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects, improving overall well-being by alleviating skin issues. The Shower+ salt shower was specially developed for the care of skin conditions like acne, providing 100% natural care.

EVERYTHING FOR THE SALT SHOWER
THE SHOWER+ STARTER SET BRINGS THE ESSENCE OF THE SEA TO YOUR SHOWER. IMMERSE YOURSELF IN A UNIQUE SHOWER EXPERIENCE AND LET THE NATURAL POWER OF SALT NURTURE AND CARE FOR YOUR SKIN.
TO THE STARTER SET




Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.